Managing users is one of the most important tasks in any software system, application, or website. Whether you are setting up a new platform, building a content management system, or running an e-commerce store, you will always need a proper structure to manage users and administrators.In this tutorial, you will learn what users and admin users are, why they matter, and how to create them step by step. This guide is written in simple language so beginners and professionals can both follow it easily.
What Are Users and Admin Users?
Users: are the general members of your platform. They usually have limited permissions. For example, they can log in, update their profile, use the services, or purchase products depending on your application.
Admin Users: are special accounts that have higher permissions. They can manage the system, create or delete users, update settings, and control sensitive data.
The separation of normal users and admin users ensures security and smooth management of the system.
Why Is It Important to Create Users and Admin Users Properly?
- Security – Different roles prevent unauthorized access to sensitive features.
- Organization – Helps in managing large systems with many members.
- Efficiency – Admins can focus on management tasks, while users enjoy services without confusion.
- Scalability – Makes it easier to expand the system when your platform grows.
Step by Step Tutorial: Creating Users and Admin Users
Here we will explain the process in a general way that can be applied to most programming frameworks, content management systems, or databases.
Step 1: Plan the Roles
Before creating users, decide what permissions each role should have. For example:
- Users: Register, login, update profile, access services.
- Admins: Manage users, update system settings, view all reports.
Step 2: Create a Database Table
Set up a table in your database to store user information. A basic structure could include:
ID:(unique identifier)NameEmailPasswordRole(example: user or admin)Created at
This role column is the key to distinguishing between normal users and admin users.
Step 3: User Registration
Allow people to sign up with their name, email, and password. By default, assign them the role of “user.”
Example:
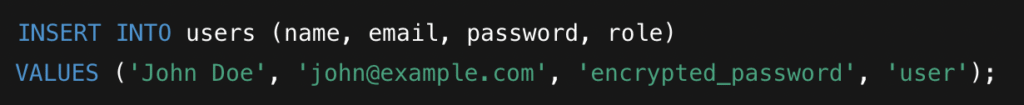
Step 4: Creating Admin Users
There are two common ways to create admin users:
- Direct Database Entry – You manually insert an admin record into the database.

2. Promotion of Existing Users – You update an existing user’s role to admin

Step 5: Login System
When users log in, check their credentials and fetch their role from the database.
- If the role is “user,” redirect them to the user dashboard.
- If the role is “admin,” redirect them to the admin panel.
Step 6: Role Based Access Control (RBAC)
This is the most important part. Always check the role before allowing any action. For example:
- Only admins should be able to delete users.
- Only admins should have access to the system settings.
- Normal users should only access their own account details.
Step 7: Test the System
Finally, test by:
- Creating a new user and logging in.
- Creating or promoting an admin and checking their privileges.
- Attempting restricted actions to ensure permissions are enforced.
Best Practices for User and Admin Management
- Always Encrypt Passwords – Never store plain text passwords. Use hashing like bcrypt.
- Use Email Verification – Helps confirm genuine accounts.
- Limit Admin Accounts – Only create admin users when absolutely necessary.
- Audit Logs – Keep a record of admin activities for accountability.
- Regular Security Updates – Protect against vulnerabilities.
Final Thoughts
Creating users and admin users is the foundation of a secure and organized application. By carefully defining roles, setting up proper database structures, and enforcing access control, you ensure that your platform runs smoothly.
When you build a clear system for users and admins, you improve both user experience and overall security. Whether you are a beginner or an experienced developer, following these steps will help you create a strong user management system.

